In this post of Python Academy, we will explore different ways to calculate Fibonacci numbers in Python. We will start with a naive recursive approach, and then move to more efficient methods.
Naive Recursive Approach
The Fibonacci sequence is defined by the recurrence relation: \(F_n = F_{n-1} + F_{n-2}\) with seed values \(F_0=0\) and \(F_1=1\).
A naive implementation of this in Python is a direct translation of the mathematical formula:
This approach is very intuitive, but it is also very slow. For n=40, it already takes a noticeable amount of time to compute. The reason for this is that the function calls itself twice for each n, leading to an exponential growth of the call stack.
Visualizing the Call Stack
To better understand the problem, let’s visualize the call stack. We can create a “talkative” version of our function that logs every call.
from rich.console import Console
from rich.tree import Tree
def fibonacci_recursive_talkative(n: int) -> int:
"""Calculate the nth Fibonacci number using a recursive approach."""
tree = Tree(f"fibonacci_recursive_talkative({n})")
def worker(n: int, tree: Tree) -> int:
"""Calculate the nth Fibonacci number using a recursive approach."""
node = tree.add(f"fibonacci_recursive({n}) called")
if n < 0:
raise ValueError("Fibonacci is not defined for negative numbers.")
if n < 2:
return n
return worker(n - 1, node) + worker(n - 2, node)
result = worker(n, tree)
Console().print(tree)
return resultFor n=6, the call tree looks like this:
fibonacci_recursive_talkative(6)
└── fibonacci_recursive(6) called
├── fibonacci_recursive(5) called
│ ├── fibonacci_recursive(4) called
│ │ ├── fibonacci_recursive(3) called
│ │ │ ├── fibonacci_recursive(2) called
│ │ │ │ ├── fibonacci_recursive(1) called
│ │ │ │ └── fibonacci_recursive(0) called
│ │ │ └── fibonacci_recursive(1) called
│ │ └── fibonacci_recursive(2) called
│ │ ├── fibonacci_recursive(1) called
│ │ └── fibonacci_recursive(0) called
│ └── fibonacci_recursive(3) called
│ ├── fibonacci_recursive(2) called
│ │ ├── fibonacci_recursive(1) called
│ │ └── fibonacci_recursive(0) called
│ └── fibonacci_recursive(1) called
└── fibonacci_recursive(4) called
├── fibonacci_recursive(3) called
│ ├── fibonacci_recursive(2) called
│ │ ├── fibonacci_recursive(1) called
│ │ └── fibonacci_recursive(0) called
│ └── fibonacci_recursive(1) called
└── fibonacci_recursive(2) called
├── fibonacci_recursive(1) called
└── fibonacci_recursive(0) called
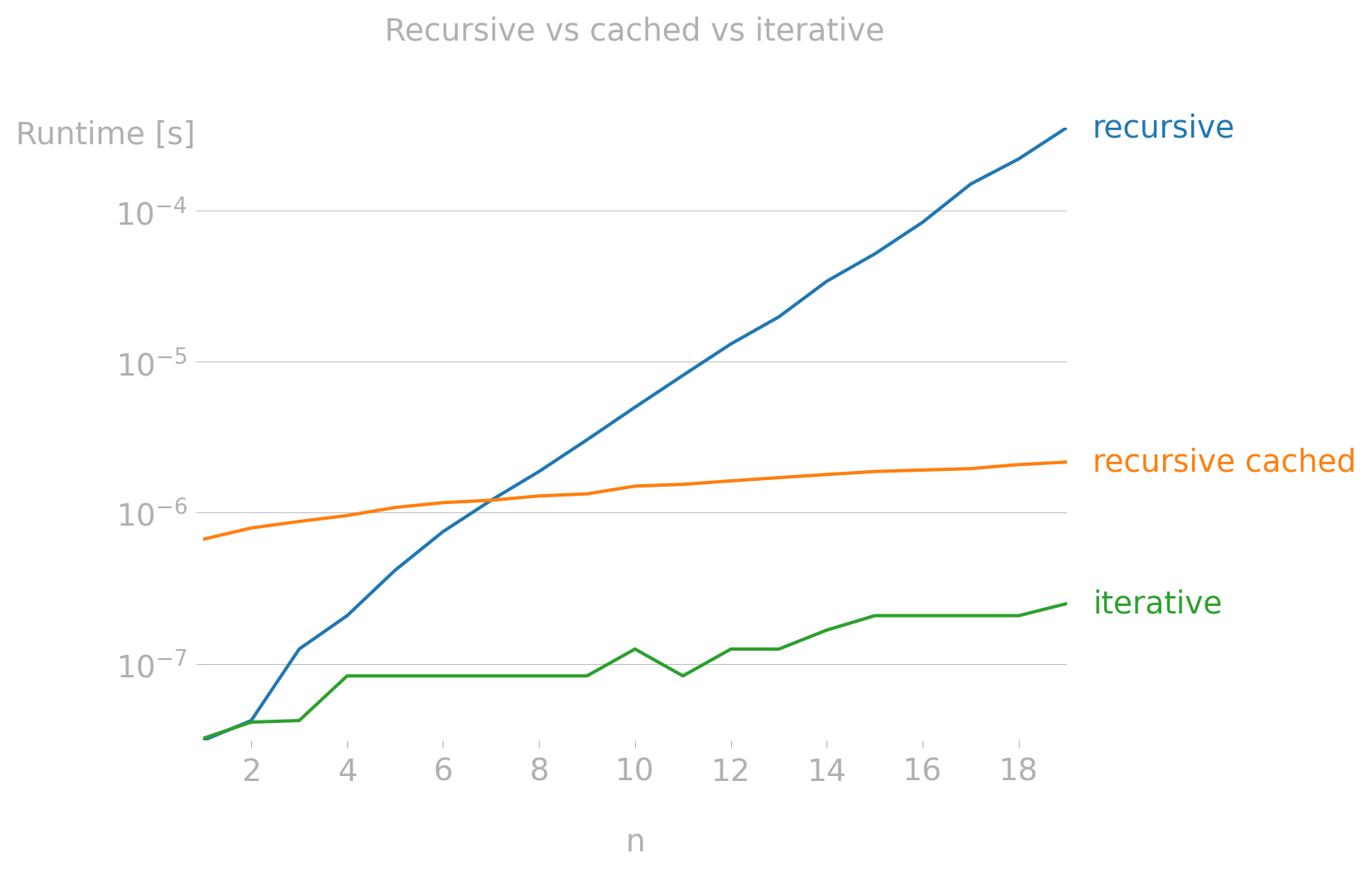
As you can see, many values are calculated multiple times. For example, fibonacci_recursive(4) is calculated twice, fibonacci_recursive(3) is calculated three times, and so on. This is the reason for the inefficiency.
Memoization
We can improve the performance by storing the results of the function calls in a cache (a dictionary). This technique is called memoization.
FIBONACCI_CACHE: dict[int, int] = {}
def fibonacci_recursive_cached(n: int) -> int:
"""Calculate the nth Fibonacci number using recursion with memoization."""
if n < 0:
raise ValueError("Fibonacci is not defined for negative numbers.")
if n < 2:
return n
if n in FIBONACCI_CACHE:
return FIBONACCI_CACHE[n]
result = fibonacci_recursive_cached(n - 1) + fibonacci_recursive_cached(n - 2)
FIBONACCI_CACHE[n] = result
return resultThis version is much faster. However, it will fail for large n (e.g., n=8_000) because of Python’s recursion depth limit.
Decorators for Caching
A more elegant way to implement memoization is by using a decorator. A decorator is a function that takes another function and extends its behavior without explicitly modifying it. Python’s functools module provides a built-in decorator lru_cache that does exactly what we need.
from functools import cache
@cache
def fibonacci_recursive_cached_decorator(n: int) -> int:
"""Calculate the nth Fibonacci number using recursion with memoization."""
if n < 0:
raise ValueError("Fibonacci is not defined for negative numbers.")
if n < 2:
return n
return fibonacci_recursive_cached_decorator(
n - 1
) + fibonacci_recursive_cached_decorator(n - 2)This is the most concise and Pythonic way to write a cached recursive Fibonacci function.
Iterative Approach
Another way to solve the problem is to use an iterative approach. This is equivalent to tail recursion optimization.
This is the most efficient way (we’ll see)to calculate Fibonacci numbers in Python. It has a linear time complexity and constant space complexity.
Performance Comparison
To compare the performance of these implementations, we can use the perfplot library. It allows us to easily benchmark different functions over a range of input sizes.
Show the code
import numba
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def fibonacci_internal_cached_decorator(n: int) -> int:
"""Calculate the nth Fibonacci number using recursion with memoization.
This version uses an internal helper function decorated with @cache.
This forces the cache to be local to this function.
"""
@cache
def helper(n: int) -> int:
"""Calculate the nth Fibonacci number using recursion with memoization."""
if n < 0:
raise ValueError("Fibonacci is not defined for negative numbers.")
if n < 2:
return n
return helper(n - 1) + helper(n - 2)
return helper(n)
fibonacci_iterative_jit = numba.njit(fibonacci_iterative)
# Force compilation
_ = fibonacci_iterative_jit(10)
def fibonacci_linalg_numpy(n):
"""Calculate the nth Fibonacci number using matrix exponentiation with NumPy."""
if n <= 0:
return 0
if n == 1:
return 1
Q = np.array([[1, 1], [1, 0]], dtype=np.uint64)
# This is the line that cannot be compiled by Numba in nopython mode
result_matrix = np.linalg.matrix_power(Q, n - 1)
return result_matrix[0, 0]Show the code
perfplot.show(
setup=lambda n: n,
kernels=[
fibonacci_recursive,
fibonacci_internal_cached_decorator,
fibonacci_iterative,
],
n_range=[i for i in range(1, 20)],
xlabel="n",
labels=[
"recursive",
"recursive cached",
"iterative",
],
title="Recursive vs cached vs iterative",
show_progress=False,
equality_check=False,
logx=False,
logy=True,
)
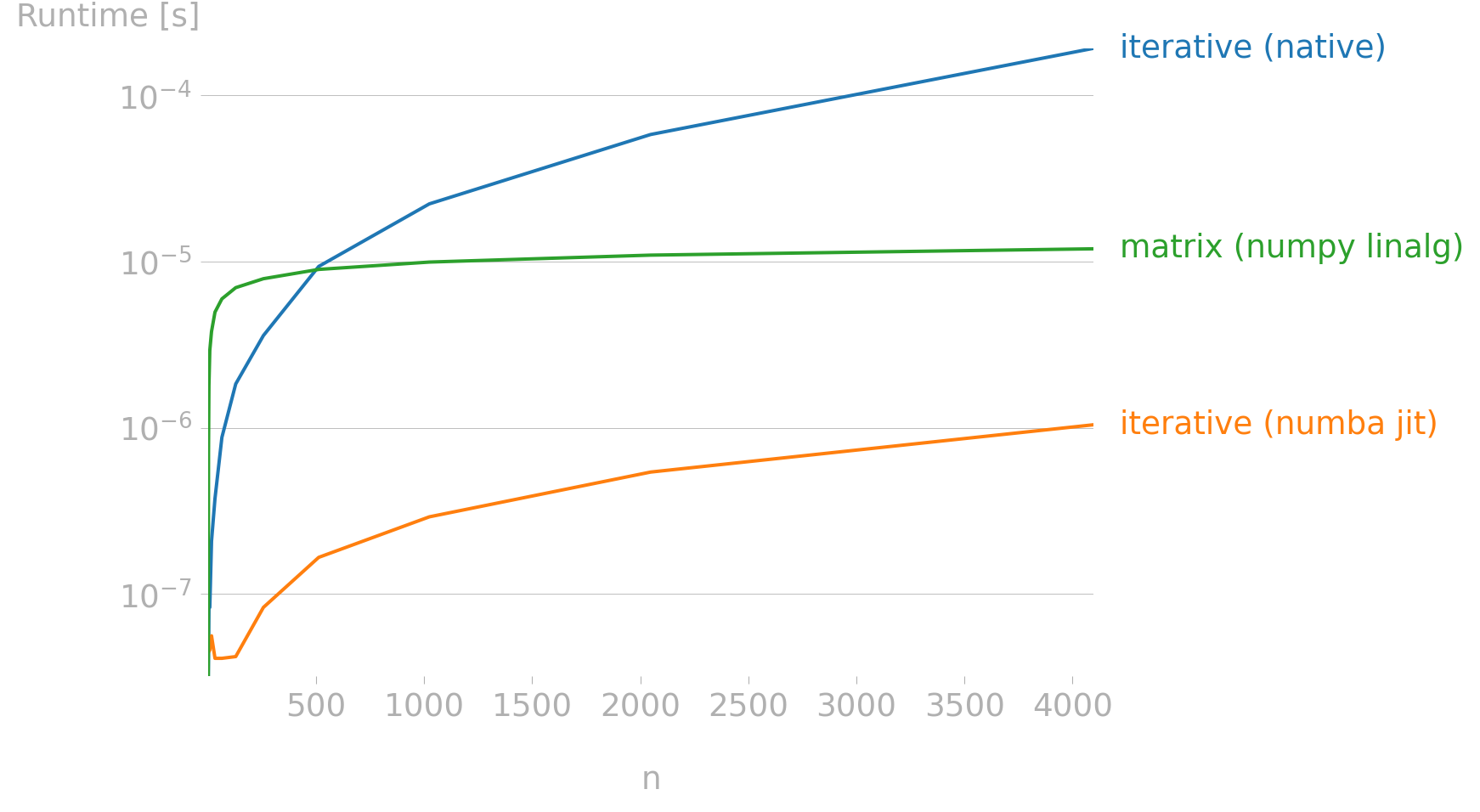
There are more advanced techniques and algorithms to compute Fibonacci numbers, below is a sneak peek for the future at two more efficient methods: using Numba’s JIT compilation and matrix exponentiation with NumPy.
Show the code
perfplot.show(
setup=lambda n: n,
kernels=[
fibonacci_iterative,
fibonacci_iterative_jit,
fibonacci_linalg_numpy,
],
n_range=[2**i for i in range(13)],
xlabel="n",
labels=[
"iterative (native)",
"iterative (numba jit)",
"matrix (numpy linalg)",
],
equality_check=False,
show_progress=False,
logx=False,
logy=True,
)
Download the whole code here.